In August 2018, NSW Health strengthened the laws that required a risk management approach to managing cooling towers.
Occupiers are required to meet The Standard, AS/NZS 3666.3 Air-handling and water systems of buildings—Microbial control, Part 3: Performance-based maintenance of cooling water systems.
The standard gives guidance on the preparation of a Legionella Risk Management Plan (RMP) but also stipulates mandatory requirements around water quality management that must be assessed.
In addition to the mandatory monthly analyses listed in the standard, Clause 3.4.2.3 details other checks required including:
The NACE method is specific to oilfield operations whilst ASTM D2688 is the primary method adopted by most companies for corrosion coupon testing of cooling towers.
Corrosion coupons are pieces of metal (usually copper and mild steel as a minimum) that have been weighed and then exposed to the system water for at least three months. Following exposure, the coupons are cleaned and weighed. The amount of metal loss is then extrapolated and presented as a corrosion rate expressed as millimeters per year (metric) or mils per year (imperial). Commentary on the coupon condition, such as etching or pit depth, provides valuable feedback on how the treatment program may be impacting on the condition of internal pipework, valves, and larger assets such as chillers. Corrosion products can also provide nutrients to bacteria such as Legionella.

ASTM D2688 details the equipment to be used, the desired flow rates, and the method of testing. In order to draw useful information, it is important that all aspects of the test method are maintained or corrosion rates may be overstated or understated.
In the same way that monthly HCC and Legionella testing provide feedback on the efficacy of a microbial control program, corrosion coupon testing is already a common practice for many companies. It is an empirical measurement that provides real data about the potential condition of assets usually unseen; the “canary in the coalmine”.
There are also real-time, online monitoring options available. Features include corrosion rate measurement by utilising metal probes and displaying/recording the current rate of corrosion for a specific metal without having to wait three months to assess the program. These can be used as a short-term remediation tool, or as an ongoing measurement that complements the water treatment program.
Your cooling tower RMP should highlight the need for corrosion coupon testing in the action plan.
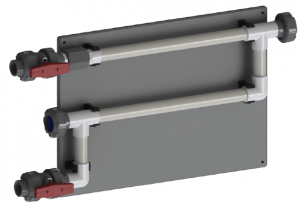
HydroChem supply corrosion coupon racks that are designed to meet the ASTM D2688 standard. We also undertake ongoing monitoring of corrosion coupons as part of the maintenance program for your cooling tower.
If you have any questions on corrosion coupon testing on your cooling tower system, please contact your Account Manager.
Best regards
Nathan Ruks, NSW State Manager M: 0411 073 259, E: nathan.ruks@hydrochem.com.au
